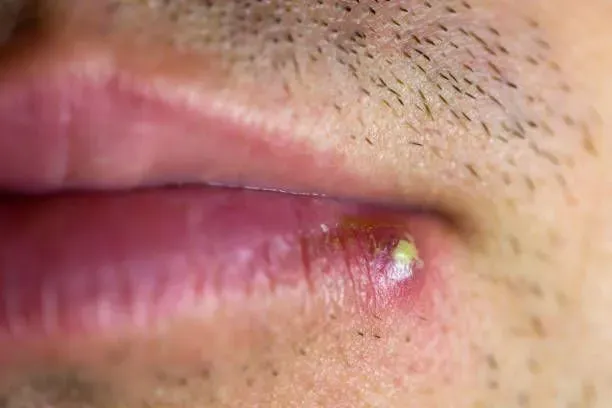
Oral shingles, a lesser-known manifestation of the varicella-zoster virus (VZV) , can significantly impact oral health and overall well-being. While shingles are commonly associated with a painful rash on the torso or face, oral shingles primarily affect the mouth and surrounding areas, leading to distinct challenges in diagnosis and treatment.
Understanding the symptoms and exploring the available treatment options can help individuals manage this condition effectively.
Oral Shingles Causes
Shingles are caused by the reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus, the same virus responsible for chickenpox. After an individual recovers from chickenpox, the virus remains dormant in nerve tissues near the spinal cord and brain. Certain triggers, such as a weakened immune system, stress, or aging, can reactivate the virus, leading to shingles.
In oral shingles, the virus reactivates in the trigeminal nerve, which supplies sensation to the face, including the mouth. This results in a localized outbreak within the oral cavity or surrounding facial regions.
Oral Shingles Symptoms

The symptoms of oral shingles can vary in severity and presentation, often mimicking other oral conditions, which complicates diagnosis.
Common symptoms include:
1. Pain and Burning Sensation
The earliest signs of oral shingles often involve pain, tingling, or a burning sensation in the mouth or face. This discomfort usually precedes the appearance of visible lesions by a few days.
2. Blister-like Lesions
Small, fluid-filled blisters can develop on the tongue, gums, inner cheeks, or palate. These blisters may burst, leaving behind open sores.
3. Swelling and Redness
Affected areas may become inflamed, swollen, and tender to the touch.
4. Difficulty Eating and Speaking
Pain and sensitivity in the mouth can make chewing, swallowing, and speaking uncomfortable.
5. Fever and Fatigue
Some individuals experience systemic symptoms such as low-grade fever, fatigue, or malaise alongside the localized oral symptoms.
6. Facial Pain or Nerve Sensitivity
In severe cases, the pain may extend to the jaw or ears, resembling dental problems or temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders.
Who Is at Risk?
Certain factors increase the likelihood of developing oral shingles:
- Age:Older adults, particularly those over 50, are more susceptible.
- Immunosuppression:Conditions such as HIV, cancer, or organ transplantation can compromise the immune system, raising the risk of reactivation.
- Stress:Chronic stress weakens the immune response, creating a favorable environment for the virus to reactivate.
- History of Chickenpox:Anyone who has had chickenpox carries the varicella-zoster virus and is at risk of developing shingles.
Potential Complications of Oral Shingles
Without timely treatment, oral shingles can lead to complications, including:
- Postherpetic Neuralgia (PHN):A condition characterized by persistent nerve pain after the shingles rash has healed.
- Secondary Infections:Open sores in the mouth are prone to bacterial infections.
- Vision Loss:If the virus spreads to the eyes (ocular shingles), it can threaten vision.
- Tooth Loss:Severe cases involving the gums may damage teeth or require dental extractions.
Read this next: Most Common Conditions Treated in Urgent Care Clinics: A Comprehensive Guide
Diagnosing Oral Shingles
Diagnosing oral shingles requires a thorough clinical evaluation. Dentists or healthcare providers may examine the patient’s symptoms and medical history. In some cases, laboratory tests, such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) or direct fluorescent antibody (DFA) tests, are used to confirm the presence of varicella-zoster virus.
Early diagnosis is crucial to prevent complications and initiate effective treatment.
Oral Shingles Treatment Options
Managing oral shingles involves a combination of antiviral medications, pain relief, and supportive care. Early intervention is key to reducing the severity and duration of symptoms.
1.Antiviral Medications
Antiviral drugs, such as acyclovir, valacyclovir, or famciclovir, are the cornerstone of shingles treatment. These medications work by inhibiting viral replication, helping to reduce pain, speed up healing, and lower the risk of complications. They are most effective when started within 72 hours of symptom onset.
2. Pain Management
Pain relief is essential for patient comfort.
Options include:
- Over-the-counter analgesics like ibuprofen or acetaminophen.
- Prescription medications such as gabapentin or pregabalin for nerve pain.
- Topical lidocaine gels or patches to numb painful areas.
3. Oral Care and Hygiene
Maintaining good oral hygiene is critical to prevent secondary infections.
Recommendations include:
- Rinsing with a mild saline solution to soothe irritation.
- Avoiding spicy, acidic, or hard foods that can exacerbate discomfort.
- Using a soft-bristled toothbrush to clean teeth gently.
4. Steroids
In some cases, corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and swelling. However, these should be used cautiously and only under medical supervision.
5. Hydration and Nutrition
Drinking plenty of fluids and consuming soft, nutrient-rich foods can help manage symptoms and support recovery.
6. Vaccination
The shingles vaccine (Shingrix) is an effective preventive measure for individuals aged 50 and older or those with weakened immune systems. While it cannot treat active shingles, it significantly reduces the risk of future outbreaks and complications.
Preventing Oral Shingles
Preventive strategies are vital, especially for at-risk populations.
- Vaccination:Getting vaccinated against shingles is the best defense.
- Stress Management:Practicing stress-reduction techniques, such as yoga, meditation, or regular exercise, can strengthen the immune system.
- Healthy Lifestyle:A balanced diet, adequate sleep, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can boost overall immunity.
Related blog: Healthy Eating Tips to Boost Your Nutrition
When to Seek Medical Attention
Prompt medical attention is recommended if you experience:
- Persistent or worsening pain despite over-the-counter remedies.
- Symptoms near the eyes or ears, which may indicate a more serious spread of the virus.
- Difficulty eating, swallowing, or speaking due to oral lesions.
- Signs of secondary infection, such as increased redness, swelling, or discharge.

Living with Oral Shingles
Coping with oral shingles can be challenging, but with the right support and treatment plan, recovery is achievable. Open communication with healthcare providers, adherence to prescribed treatments, and self-care measures can significantly improve outcomes.
Related blog: Finding Immediate Medical Help: Your Ultimate Guide to Locating the Best Urgent Care Near You
Get Treated Today
If you’re experiencing unexplained oral pain or lesions, it’s important to seek treatment immediately. At UrgiClinic Urgent Care, we offer prompt, walk-in medical services without the long wait times. Our clinic is open seven days a week, from 9:00 AM to 9:00 PM, providing comprehensive care for various health concerns, including oral health issues.