What is Mild Tendonitis: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments
Tendonitis is a common condition that occurs when a tendon becomes inflamed due to overuse, strain, or injury.
While severe cases can lead to prolonged pain and mobility issues, mild tendonitis is more manageable but still requires proper care. Understanding the causes of mild tendonitis, recognizing symptoms early, and following effective treatment methods can help prevent complications and ensure a swift recovery.
What is Mild Tendonitis?
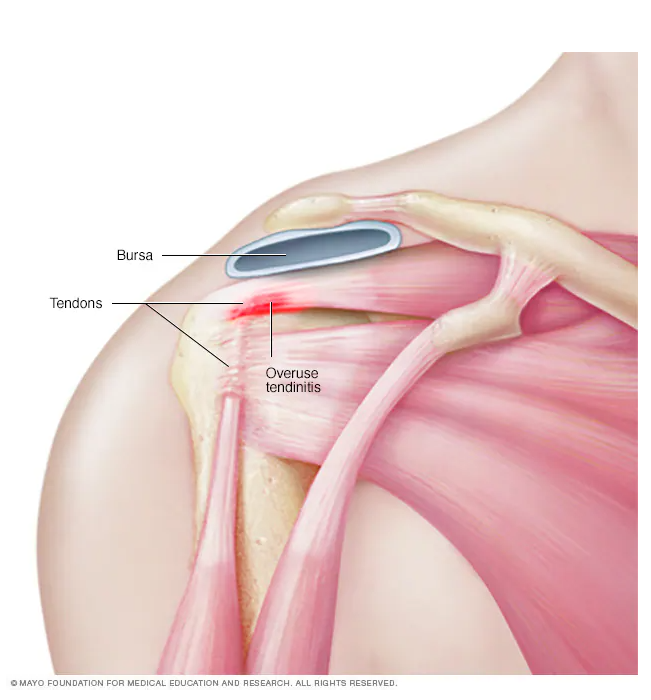
Mild tendonitis refers to a minor inflammation of the tendons, which connect muscles to bones.
This condition can cause discomfort, stiffness, and swelling in the affected area, but it does not result in significant tendon damage. Mild cases often improve with rest and conservative treatments, making early intervention crucial.
Common Causes of Mild Tendonitis
Several factors contribute to the development of mild tendonitis, including:
- Repetitive Movements – Engaging in repetitive motions like typing, lifting, or playing sports can strain tendons over time, leading to inflammation. Repetitive stress injuries are a common cause of tendonitis.
- Improper Technique – Poor posture or incorrect exercise form places excessive strain on tendons, increasing the risk of injury and inflammation.
- Sudden Increase in Activity – Rapidly increasing the intensity or duration of physical activity can overload tendons. Failing to gradually build strength and endurance can lead to tendon inflammation and injury.
- Aging – As we age, tendons lose elasticity, making them more vulnerable to inflammation and injury. The Hospital for Special Surgery highlights that age-related changes in tendon structure significantly contribute to tendonitis.
- Medical Conditions – Chronic conditions like arthritis and diabetes can increase the likelihood of developing tendonitis. These systemic diseases can weaken tendons and contribute to ongoing inflammation.
These factors emphasize the importance of proper technique, gradual activity increases, and overall tendon health to prevent discomfort and long-term complications.
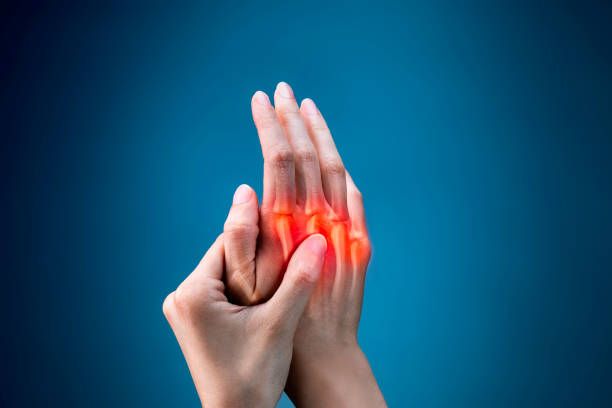
Symptoms of Mild Tendonitis
The symptoms of mild tendonitis typically develop gradually and may include:
- Mild pain and tenderness near a joint
- Swelling or warmth in the affected area
- Stiffness or decreased range of motion
- Discomfort that worsens with movement but improves with rest

Treatment for Mild Tendonitis
The following treatment methods can help alleviate symptoms and promote healing:
1. Rest and Activity Modification
Reducing activities that strain the affected tendon is essential. Avoid repetitive motions and take frequent breaks to prevent worsening the condition. If pain persists, consider adjusting your daily activities to reduce stress on the tendon.
2. Ice Therapy
Applying an ice pack to the inflamed area for 15-20 minutes every few hours can reduce swelling and pain. Ice therapy helps constrict blood vessels, limiting inflammation and providing relief.
3. Compression and Elevation
Using a compression bandage can provide support, while keeping the affected area elevated can minimize swelling. Proper compression can also prevent excessive movement, which may aggravate the condition.
4. Stretching and Strengthening Exercises
Once the initial pain subsides, engaging in gentle stretching and strengthening exercises can improve tendon flexibility and prevent future injuries.
Some effective exercises include:
- Eccentric exercises – Controlled lengthening movements to strengthen tendons
- Range-of-motion exercises – Gentle stretches to restore movement
- Resistance training – Using light weights or resistance bands to build strength
5. Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or naproxen can help manage pain and inflammation. However, they should be used as directed and not relied upon as a long-term solution.
When to Seek Urgent Care
While mild tendonitis often heals with self-care, you should seek medical attention if:
- Pain persists for more than a few weeks despite treatment
- The affected area becomes significantly swollen or bruised
- You experience weakness or loss of movement in the joint
- There is a noticeable lump or thickening around the tendon
In some cases, untreated mild tendonitis can progress into chronic tendonitis or lead to a tendon tear, requiring more intensive treatments like physical therapy or even surgery.
Preventing Mild Tendonitis
Taking preventive measures can help reduce the likelihood of developing mild tendonitis. Consider the following tips:
- Warm-up properly – Before exercising, engage in a thorough warm-up to prepare muscles and tendons.
- Use ergonomic tools – Proper workstation setup can prevent repetitive strain injuries in office settings.
- Strengthen surrounding muscles – Building strength in adjacent muscle groups can reduce the strain on tendons.
- Take breaks – If performing repetitive tasks, short breaks can minimize overuse injuries.
- Wear proper footwear – Shoes with adequate support can prevent excessive stress on lower-body tendons.
Walk-in With Us
If you're experiencing persistent discomfort or want professional guidance on mild tendonitis treatment, UrgiClinic Urgent Care is here to help.
Our experienced healthcare professionals can assess your condition and recommend the best course of action. Walk-in with us today for expert care and a personalized treatment plan.